Structure
JJJJ.PPPPPPP.SSSSSSSS
- JOSE
- Payload
- Signature
RFCs
Usage
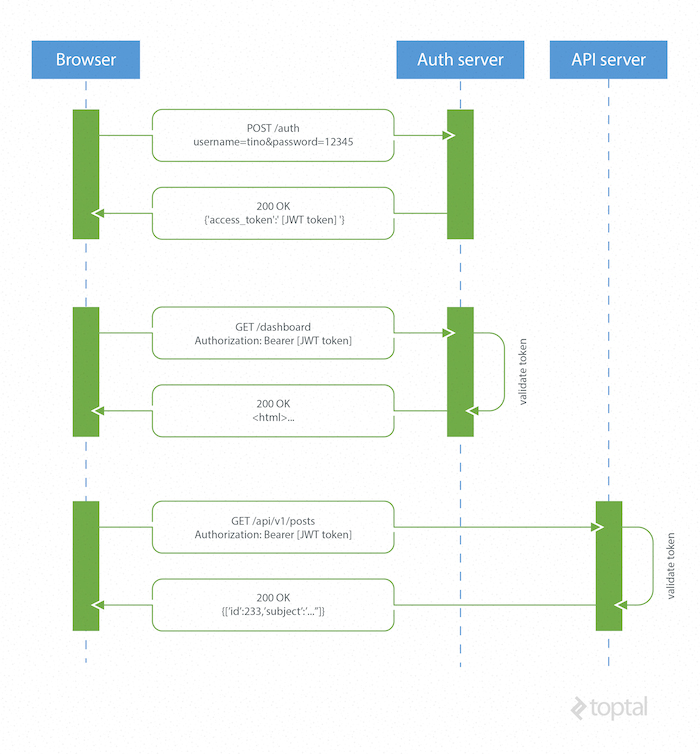
Validation Algorithm
7.2. Validating a JWT
When validating a JWT, the following steps are performed. The order of the steps is not significant in cases where there are no dependencies between the inputs and outputs of the steps. If any of the listed steps fail, then the JWT MUST be rejected – that is, treated by the application as an invalid input.
Verify that the JWT contains at least one period (‘.’) character.
Let the Encoded JOSE Header be the portion of the JWT before the first period (‘.’) character.
Base64url decode the Encoded JOSE Header following the restriction that no line breaks, whitespace, or other additional characters have been used.
Verify that the resulting octet sequence is a UTF-8-encoded representation of a completely valid JSON object conforming to RFC 7159 [RFC7159]; let the JOSE Header be this JSON object.
Verify that the resulting JOSE Header includes only parameters and values whose syntax and semantics are both understood and supported or that are specified as being ignored when not understood.
Determine whether the JWT is a JWS or a JWE using any of the methods described in Section 9 of [JWE].
Depending upon whether the JWT is a JWS or JWE, there are two cases:
If the JWT is a JWS, follow the steps specified in [JWS] for validating a JWS. Let the Message be the result of base64url decoding the JWS Payload.
Else, if the JWT is a JWE, follow the steps specified in [JWE] for validating a JWE. Let the Message be the resulting plaintext.
If the JOSE Header contains a “cty” (content type) value of “JWT”, then the Message is a JWT that was the subject of nested signing or encryption operations. In this case, return to Step 1, using the Message as the JWT.
Otherwise, base64url decode the Message following the restriction that no line breaks, whitespace, or other additional characters have been used.
Verify that the resulting octet sequence is a UTF-8-encoded representation of a completely valid JSON object conforming to RFC 7159 [RFC7159]; let the JWT Claims Set be this JSON object.
Python Implementations
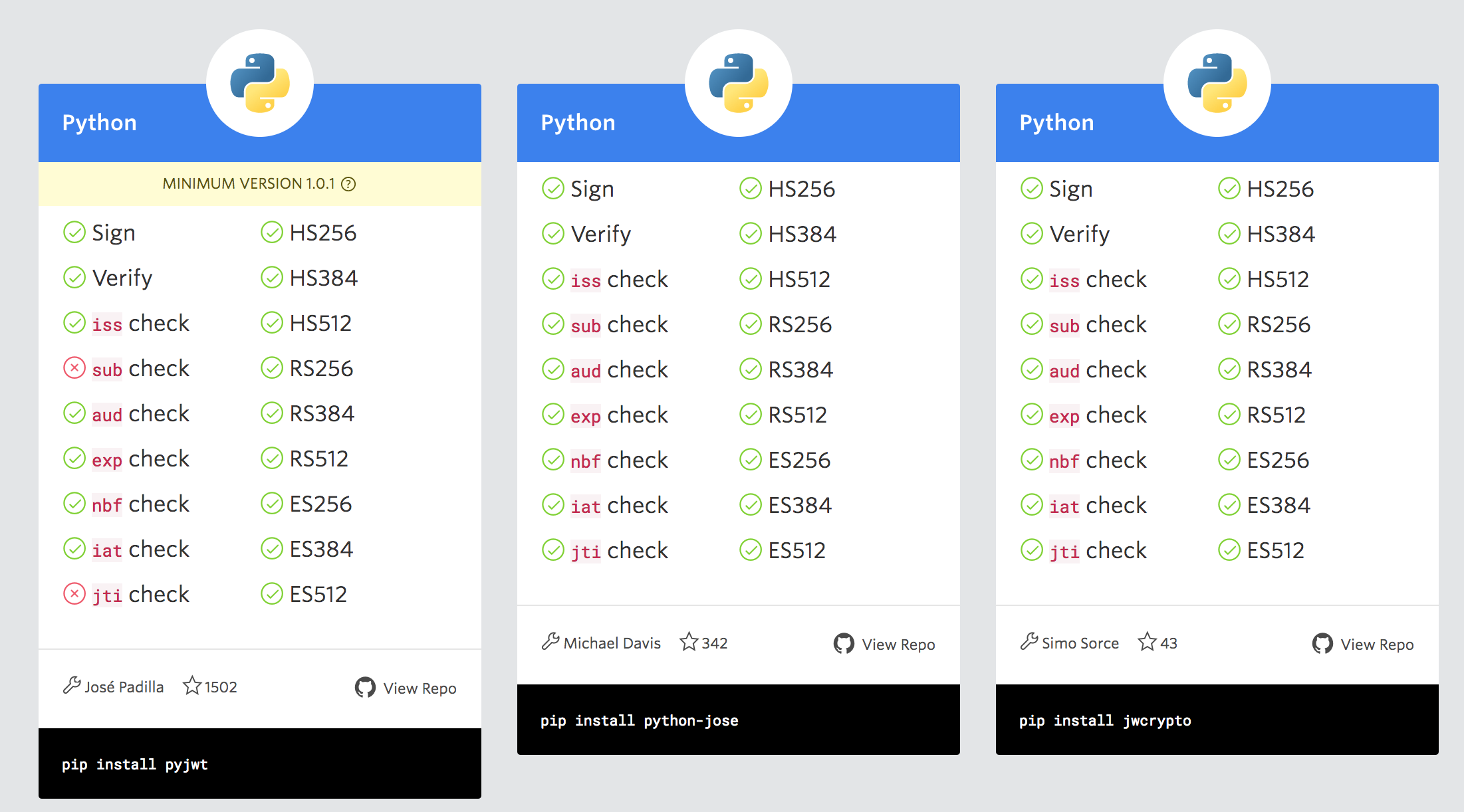
jwt.io has a big list of major open source implementations by programming language
Python community has three:
- https://github.com/jpadilla/pyjwt
- https://github.com/mpdavis/python-jose
- https://github.com/latchset/jwcrypto
// official sample from RFC7515 in C#
static byte [] base64urldecode(string arg)
{
string s = arg;
s = s.Replace('-', '+'); // 62nd char of encoding
s = s.Replace('_', '/'); // 63rd char of encoding
switch (s.Length % 4) // Pad with trailing '='s
{
case 0: break; // No pad chars in this case
case 2: s += "=="; break; // Two pad chars
case 3: s += "="; break; // One pad char
default: throw new System.Exception(
"Illegal base64url string!");
}
return Convert.FromBase64String(s); // Standard base64 decoder
}
As per the example code above, the number of ‘=’ padding characters that needs to be added to the end of a base64url-encoded string without padding to turn it into one with padding is a deterministic function of the length of the encoded string. Specifically, if the length mod 4 is 0, no padding is added; if the length mod 4 is 2, two ‘=’ padding characters are added; if the length mod 4 is 3, one ‘=’ padding character is added; if the length mod 4 is 1, the input is malformed.
# jwcrypto implementation of JWS Appendix C
# this is a naive translation from C#, not pythonic
def base64url_decode(payload):
l = len(payload) % 4
if l == 2:
payload += '=='
elif l == 3:
payload += '='
elif l != 0:
raise ValueError('Invalid base64 string')
return urlsafe_b64decode(payload.encode('utf-8'))
# python-jose implementation
def base64url_decode(input):
"""Helper method to base64url_decode a string.
Args:
input (str): A base64url_encoded string to decode.
"""
rem = len(input) % 4
if rem > 0:
input += b'=' * (4 - rem)
return base64.urlsafe_b64decode(input)
# pyjwt's implementation has well considered the python2/3 about string and bytes
# that probably explained well why it get most stars in github
def base64url_decode(input):
if isinstance(input, text_type):
input = input.encode('ascii') ## can utf-8 here better?
rem = len(input) % 4
if rem > 0:
input += b'=' * (4 - rem)
return base64.urlsafe_b64decode(input)
from the repo structure
Snippet
# example encode header
import base64
def jwt_encode_header(header):
return base64.urlsafe_b64encode(
header if isinstance(header, bytes)
else header.encode('utf-8')).replace(
b'=', b'')
header = '{"typ": "JWT", "alg": "HS256"}'
jose = jwt_encode_header(header) # JSON Object Signing & Encryption
>>> b'eyJ0eXAiOiAiSldUIiwgImFsZyI6ICJIUzI1NiJ9'